Abstract
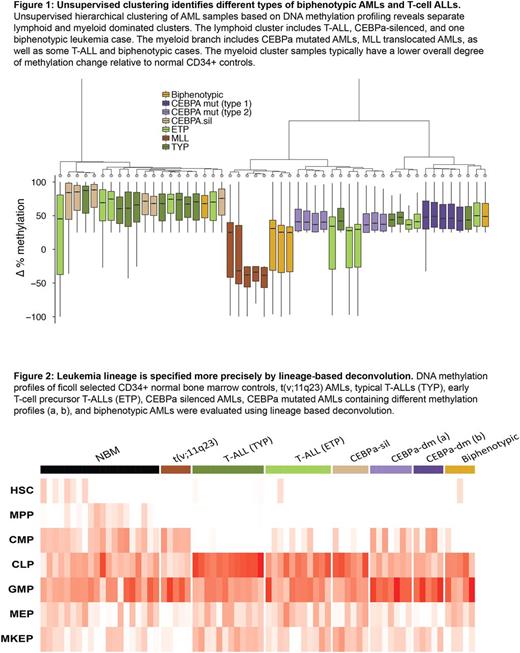
Hematopoietic differentiation is characterized by the organized epigenetic reprogramming of hematopoietic stem cells to terminally differentiated cells. Acute leukemias represent a disruption of this process and are categorized into myeloid and lymphoid subtypes on the basis of surface marker patterns identified by flow cytometry. Biphenotypic and other poorly specified leukemias such as early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemias (ETP T-ALLs) highlight the limitations of this technology. Here we describe a novel approach to characterize leukemia lineage on the basis of epigenetic characteristics. Using model-based deconvolution, we show that DNA methylation profiling and ATAC-seq chromatin accessibility maps can be used to specify leukemia lineage characteristics more precisely. On in-vitro mixtures of purified cells, it can quantitatively determine sample composition with R2 = 0.89. Extending this method to evaluate primary leukemia samples, we show that ETP T-ALLs exhibit a mixture of lineage characteristics that varies by patient. Typical T-ALL patient samples exhibit predominantly lymphoid characteristics most similar to the common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) stage. In contrast, ETP T-ALL cases exhibit a mixture of myeloid and lymphoid features, with some showing dominant CLP features, some a mix of both CLP and granulocytic macrophage progenitor (GMP) characteristics, and one with dominant GMP features. Biphenotypic leukemias also contained CLP dominant, GMP dominant, and mixed cases. CEBPa-silenced AMLs, which had previously been described as exhibiting a T-cell like phenotype, exhibited dominant CLP characteristics in contrast to other AMLs that exhibit dominant GMP features. In the future, we hope to adapt this method to assist in determining whether myeloid or lymphoid directed therapy should be used for leukemias with ambiguous lineage characteristics.
Levine: Qiagen: Equity Ownership; Roche: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Qiagen: Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal